Shebang Support
Shebang is a versatile tool designed to execute scripts written in various scripting languages including Shell, Perl, Python, and more. Runme integrates Shebang to enable users to run the script of their choice directly from the Markdown file in their preferred programming language.
Prerequisites
Before proceeding with the integration of Shebang in Runme, ensure that Runme is properly installed on your system. This is a crucial step to guarantee the smooth execution of your runbooks
Run your Code with Runme in VS Code Using Shebang
Runme gives you the power to run your code right inside your Markdown file in VS Code without having to switch to a terminal. To do this, follow the steps below:
- Click on the +Code icon.
- Enter the script you would like to run.
- Click on the Select Cell Language Mode and select a language of your choice.
- Now click on Execute Cell
Configuring Shebang Custom Interpreter in VS Code
Before proceeding with the integration of Shebang in Runme, ensure that Runme is properly installed on your system. This is a crucial step to guarantee the smooth execution of your runbooks
Alternatively, if you would love to run your code using your specified interpreter version, you can achieve that using the custom interpreter feature. This allows you to configure the environment for running code directly within your editor, making your coding experience much smoother and easier.
Follow the steps below to set up the Shebang custom interpreter in VS Code:
- Open your script (Markdown file) in VS Code
- Click on Configure menu at the buttom right of your code block
- Click on Advanced
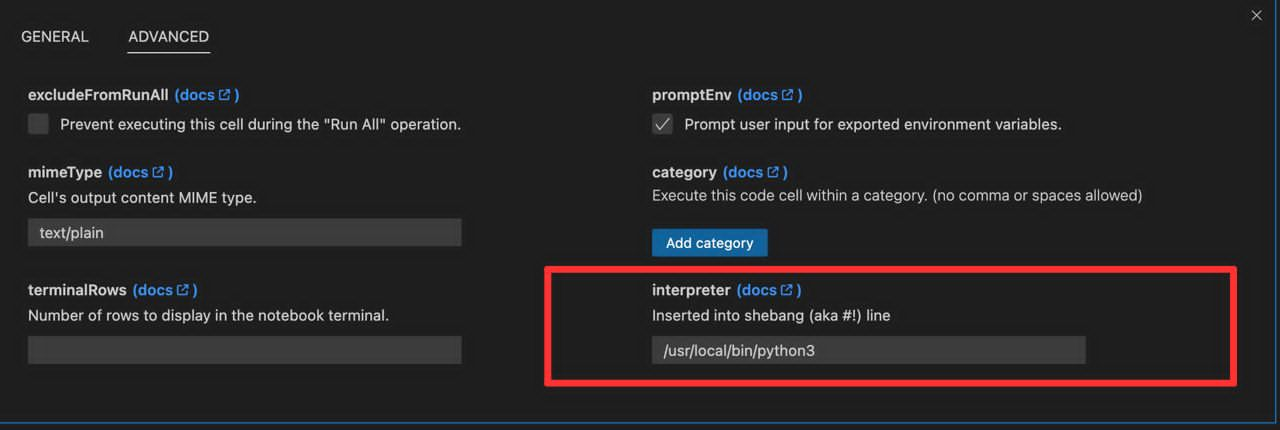
- Set the path to the system interpreter of your choice.
- Close the modular
- Execute the Runme command:
# short for "runme tui" is
runme
Examples of Shebang Lines for Different Languages
We have attached some scripts in various languages as seen below to enable you to test how Runme works in your VS Code.
Each of the following examples, written in Python, Ruby, Bash, and Node.js (JavaScript), accomplishes the same task: they define a greeting ("Hello, World!"), obtain the current date and time, and then combine these into a single message. The primary difference lies in the syntax and functions/methods used for date and time formatting in each language.
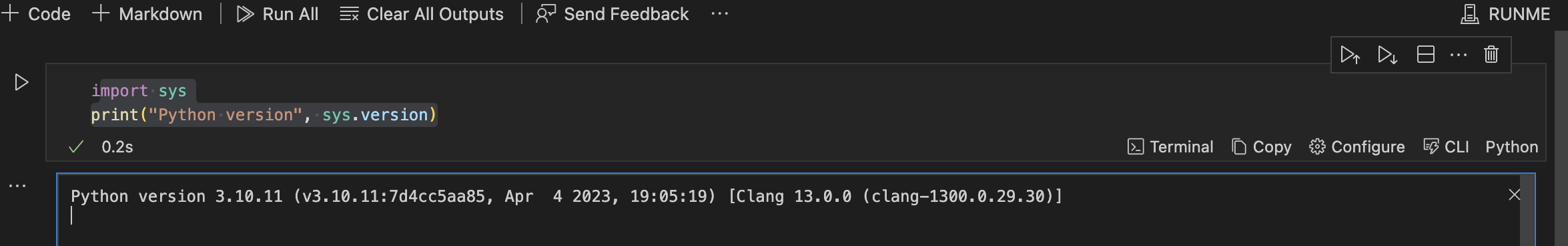
Python
To run the Python code, you need to set the path to the Python interpreter, which is /usr/bin/python3, in the advanced section of your configuration in your code block.
import datetime
# Define a variable for the greeting
greeting = "Hello, World!"
# Get the current date and time
currentDateTime = datetime.datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
# Concatenate the greeting with the current date and time
fullGreeting = greeting + " It's now " + currentDateTime
# Output the full greeting
print(fullGreeting)
Bash
To use Bash, you need to set the Interpreter to point to the Bash interpreter, which is /usr/bin/bash, in the advanced section of your configuration in your code block.
# Define a variable for the greeting
greeting="Hello, World!"
# Get the current date and time
currentDateTime=$(date '+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
# Concatenate the greeting with the current date and time
fullGreeting="$greeting It's now $currentDateTime"
# Output the full greeting
echo $fullGreeting
Ruby
To use Ruby, you need to add the path to the Ruby interpreter, which is /usr/bin/ruby, in the advanced section of your configuration in your code block.
# Define a variable for the greeting
greeting = "Hello, World!"
# Get the current date and time
currentDateTime = Time.now.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
# Concatenate the greeting with the current date and time
fullGreeting = "#{greeting} It's now #{currentDateTime}"
# Output the full greeting
puts fullGreeting
PHP
To use PHP, you need to add the path to the PHP interpreter, which is /usr/bin/php, in the advanced section of your configuration in your code block..
<?php
// PHP Script Example: Greeting with Date and Time
// Define a variable for the greeting
$greeting = "Hello, World!";
// Get the current date and time
$currentDateTime = date('Y-m-d H:i:s');
// Concatenate the greeting with the current date and time
$fullGreeting = $greeting . " It's now " . $currentDateTime;
// Output the full greeting
echo $fullGreeting;
?>
Node
To use Node.js, you need to add the path to the node interpreter, which is /usr/bin/node, in the advanced section of your configuration in your code block.
// Define a variable for the greeting
const greeting = "Hello, World!";
// Get the current date and time
const currentDateTime = new Date()
.toISOString()
.replace("T", " ")
.substring(0, 19);
// Concatenate the greeting with the current date and time
const fullGreeting = `${greeting} It's now ${currentDateTime}`;
// Output the full greeting
console.log(fullGreeting);
List of Auto-Detected Language Runtimes
Runme auto-detects runtimes based on the language selection per cell.
| Name | LanguageIDs | Runtime (first match wins) |
|---|---|---|
| Bash Shell | bash | bash |
| Windows cmd.exe | cmd | cmd |
| Windows cmd.exe | dos | cmd |
| Fish Shell | fish | fish |
| Javascript | javascript, js, jsx, javascriptreact | node |
| Korn Shell | ksh | ksh |
| Lua | lua | lua |
| Perl | perl | perl |
| PHP | php | php |
| PowerShell | powershell | powershell |
| Python | python, py | python3, python |
| Ruby | ruby, rb | ruby |
| Rust | rust, rs | rust-script |
| Unix Shell | shell, sh | bash, sh |
| Typescript | typescript, ts, tsx, typescriptreact | ts-node, deno, bun |
| Z Shell | zsh | zsh |
Missing a language? Please raise an issue.
Combining Multiple Languages in Your Notebook
It's possible to combine multiple languages in a single notebook by using different shebang lines for each script block. For an example of a notebook with multiple languages, see the Shebang Notebooks example on GitHub.