Embedded Github Action UI
💡 Be sure to install Runme for VS Code first
GitHub Actions provides a robust CI/CD platform for automating development tasks. Runme supports only manual workflows in GitHub Actions, allowing on-demand tasks like targeted releases and incident responses. Users can trigger these workflows in Runme by pasting specific GitHub URLs, and after inputting the required parameters, execute the workflow directly.
Workflow Types
- Events that occur in your workflow's repository
- Events that occur outside of GitHub and trigger a repository_dispatch event on GitHub
- Scheduled times
- Manual
Currently, Runme only supports manual workflows; they are helpful to trigger jobs on demand, some common use cases are:
- Targeted releases: Deploy specific versions of artifacts to specific environments (production, testing, staging) on demand or after thorough testing or approval.
- Overwrite a scheduled task workflow: Sometimes, you may want to override the schedule and trigger the workflow manually.
- Trigger a testing pipeline: Initiate specific code or infrastructure verification testing workflows. This allows developers or quality assurance teams to trigger comprehensive tests when needed, ensuring adequate coverage.
- Incident response: Reduce risk during an incident by triggering an incident response workflow. It helps mitigate the problem by including diagnostic scripts, notifying the immediate response team, or initiating remedial action.
- User Interaction Workflows: GitHub Actions can be triggered manually to facilitate user interactions, such as starting a build or initiating a specific process based on user input. Useful for workflows involving user requests, feedback, or custom actions.
- Experimental or One-off Tasks: Sometimes, you may need to run a workflow for an experimental or one-off task that doesn't require automation or a predefined trigger. Manually triggering the workflow provides flexibility in executing such tasks.
In general, being able to run a GitHub Action manually gives you control over workflows by adding an extra layer of flexibility to your CI/CD and automation processes.
How To Use It
Use the workflow_dispatch event to specify your manually triggered workflow, you can optionally specify inputs that are passed to the workflow. The triggered workflow receives the inputs in the inputs context
See an example of a manually triggered workflow:
name: My manual worfklow
on:
workflow_dispatch:
inputs:
releaseVersion:
description: "Runme release version"
required: true
type: string
default: latest
releaseType:
description: "Release Type"
required: true
type: choice
default: "patch"
options:
- patch
- minor
- major
releaseChannel:
description: "Release Channel"
required: true
type: choice
default: stable
options:
- stable
- edge
publishMarketplace:
description: "Publish on Visual Studio Marketplace?"
required: true
type: choice
default: "yes"
options:
- "yes"
- "no"
publishOpenVSX:
description: "Publish on Open VSX Registry?"
required: true
type: choice
default: "yes"
options:
- "yes"
- "no"
jobs:
release:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
env:
REPOSITORY: runme
steps:
- name: Print inputs
run: |
echo "${{ toJSON(github.event.inputs) }}"
The above YAML file specifies a simple manual triggered workflow file with inputs: releaseVersion, releaseType, releaseChannel, publishMarketplace, publishOpenVSX, and a job that prints the values for each input in JSON format.
Use Runme To Trigger A Manual Workflow
Currently, there are two ways to indicate Runme to run a GitHub Action:
- GitHub repository source URL
https://github.com/organization/repository/blob/main/.github/workflows/workflow.yml - GitHub workflow URL
https://github.com/organization/repository/actions/workflows/workflow.yml
If you paste a URL following any of those formats in any Markdown file, Runme will understand you want to run a manually triggered GitHub Action. If the file specifies inputs, a convenient form is displayed to specify the values, they will be displayed according to the type of input:
- Choice: Drop-down list
- String: Input text
To execute the action, you need access to the repository and sign in using your GitHub account by authorizing Runme from within VS Code
Once you are signed in, you should be able to see the workflow file like the following:
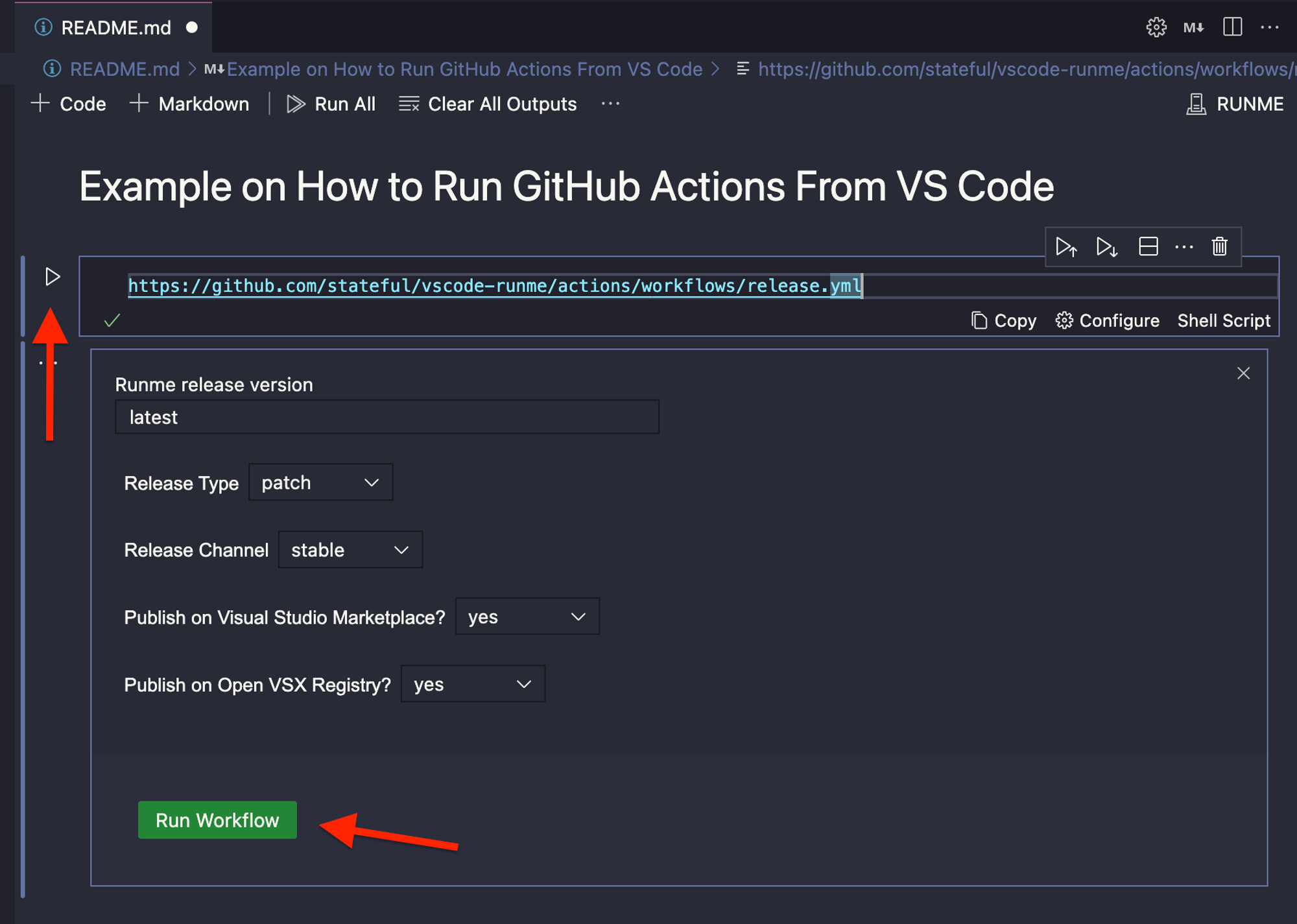
In the above example, we have a workflow action with inputs, once you specify them, you can click Run Workflow to trigger the action. Once you trigger the action, you will see in real-time the status of the execution of the workflow, just like the original GitHub action interface.
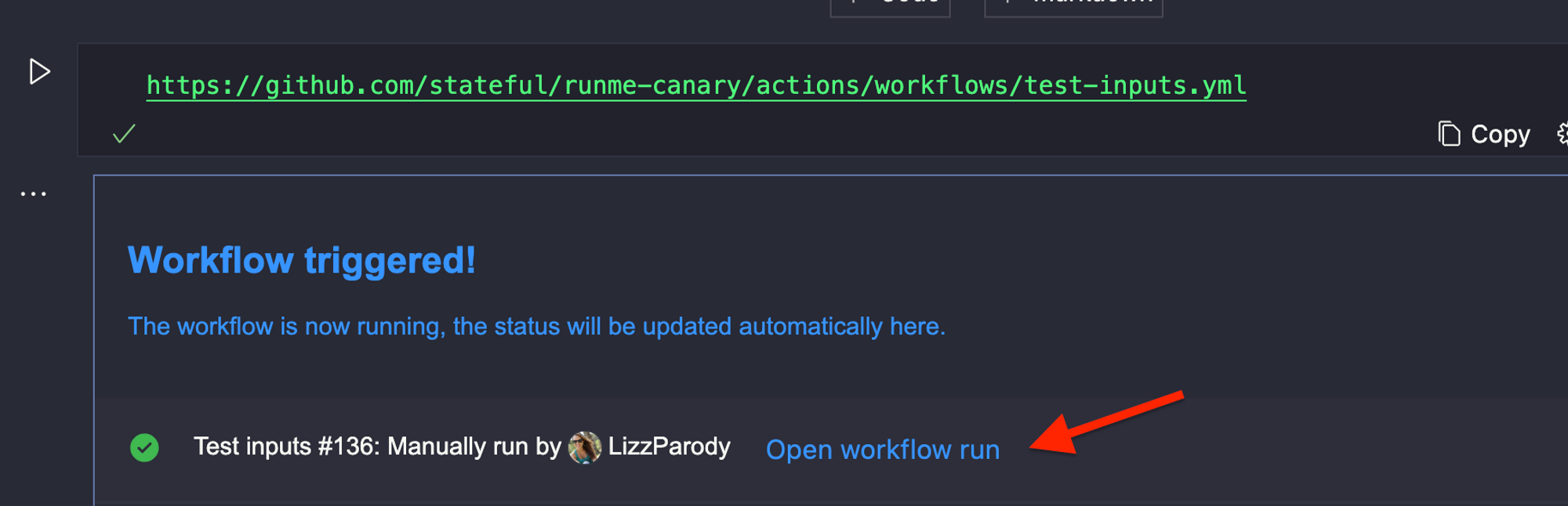
If you click Open workflow run, a browser window will be opened with the detailed logs of the triggered workflow.
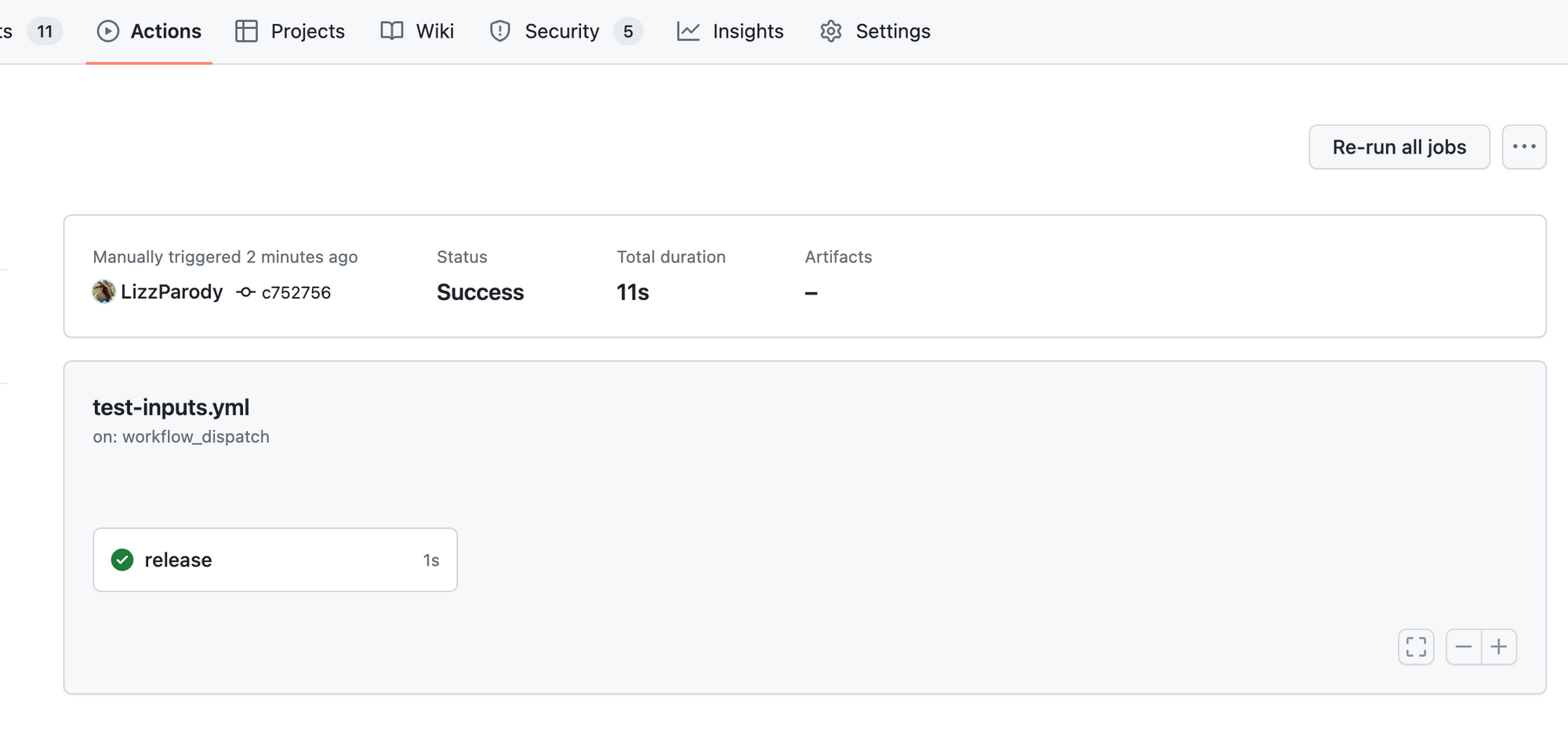
In the next Runme version release, we will display workflow run details in real-time. We believe Runme is a great companion to the official GitHub Actions extension.