Hello world
Runme makes it easy to run bash scripts directly within your Markdown files. With Runme, you can create, manage, and run scripts to automate repetitive tasks, saving time and effort.
This is not just limited to bash; Runme supports scripting in various languages like PowerShell, Python, and more. This flexibility allows you to tailor automated solutions to your specific requirements.
Setting Up Your Environment
To get started with Bash scripts in Runme, you are required to first install and configure Runme on your VS Code editor. If you do not have Runme on VS Code installed yet, proceed to the Extension tab of your VS Code and search for “Runme DevOps Notebook.”
You can configure your code editor to make Runme your default Markdown viewer. This means you .md will be displayed as a runbook whenever you open a Markdown.
Writing Your First Bash Script in Runme
Runme integrates easily with Bash scripts via the Shebang feature, which allows you to run any script you choose directly from the Markdown file in your preferred programming language.
This section will provide a step-by-step guide to creating a simple bash script within a Markdown file and executing it with Runme.
Let’s get started.
- Create a new folder and open it with your VS code. In your VS code, create a new README.md file.
- Click on the + Code icon
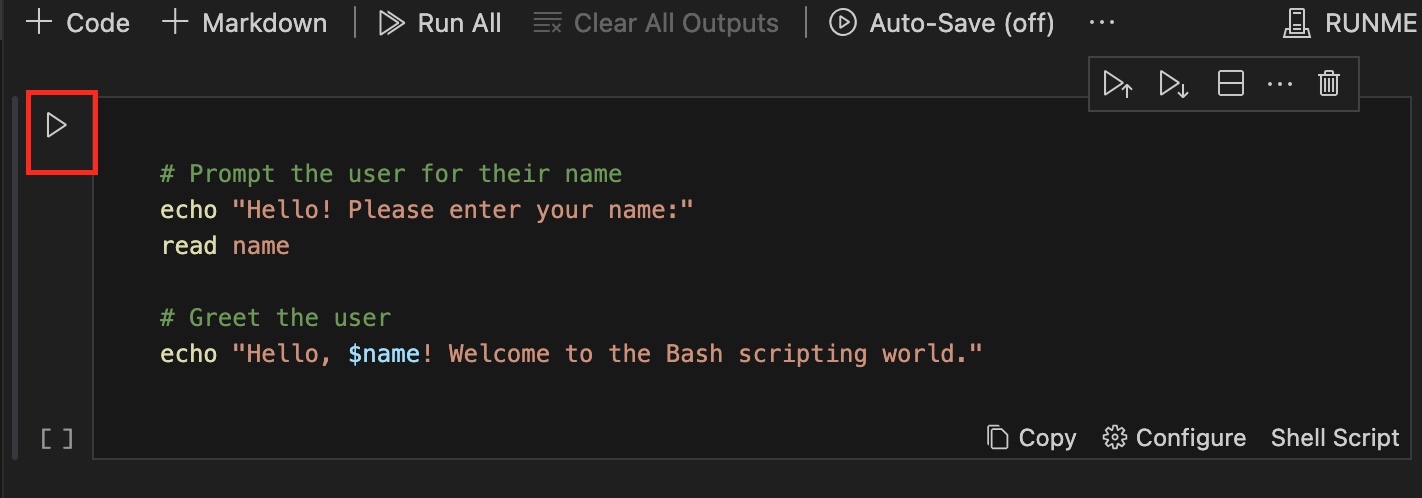
- Enter the script you want to run. For this tutorial, we will be using the simple bash script below.
echo "Hello! Please enter your name"
read name
#Greet the user
echo "Hello, $name! Welcome to the Bash Scripting World"
- Click on the programming language at the button of the cell. This will display a list of supported languages. .
- Search for Shell script.
- Now click on the Run button beside your script to execute it.
After an execution time of 2.3 seconds, you will get a similar output:
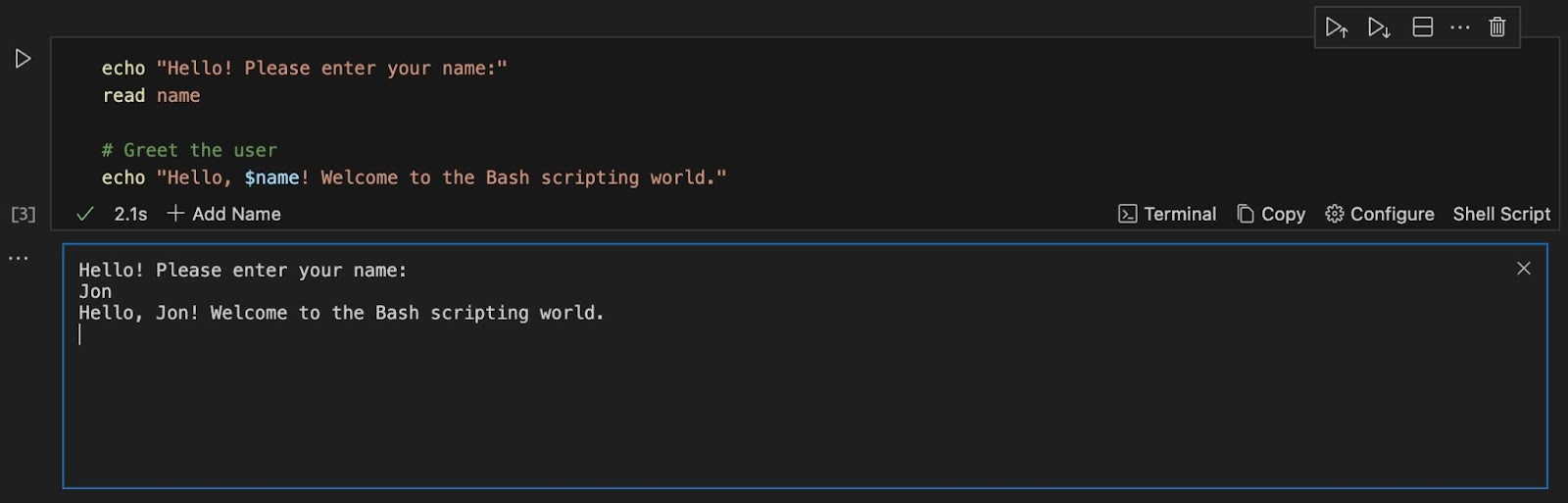 You have successfully executed your first bash script with Runme!🎉
You have successfully executed your first bash script with Runme!🎉
Runme makes it incredibly easy! Previously, you would have to create a .sh file to execute bash scripts, but with Runme, you do not need to create a new file from scratch. All you need to do is install the Runme extension in VS Code, and you can save yourself the stress of environment issues, as bash scripts run swiftly in Runme regardless of your machine's environment and operating system.
Let’s dive into more advanced bash scripting actions.
Advanced Bash Scripting Techniques in Runme
Bash scripts have several advanced techniques that can be integrated with Rume. In this section, we will explore some of the advanced features of bash scripting and how they can be integrated with Runme.
-
Variable Manipulation:
Variable manipulation involves modifying or extracting parts of a variable’s value to suit your needs without changing the original data. This can be done and executed in your Markdown file without external dependencies.
The image below provides an example of how a user can manipulate variables in bash scripts in Runme and the corresponding output the user will get in the terminal.
Run the script below to understand how Variable manipulation works.
sentence="The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog"
echo ${sentence:4:5}
first_name="John"
last_name="Doe"
full_name="$first_name $last_name"
echo $full_name
sentence="The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog"
echo ${sentence/brown/yellow}
name="Alice"
echo $name | tr '[:lower:]' '[:upper:]'
echo $name | tr '[:upper:]' '[:lower:]'
echo ${#name}
The image below provides a visual representation of the output of this script when it is executed.
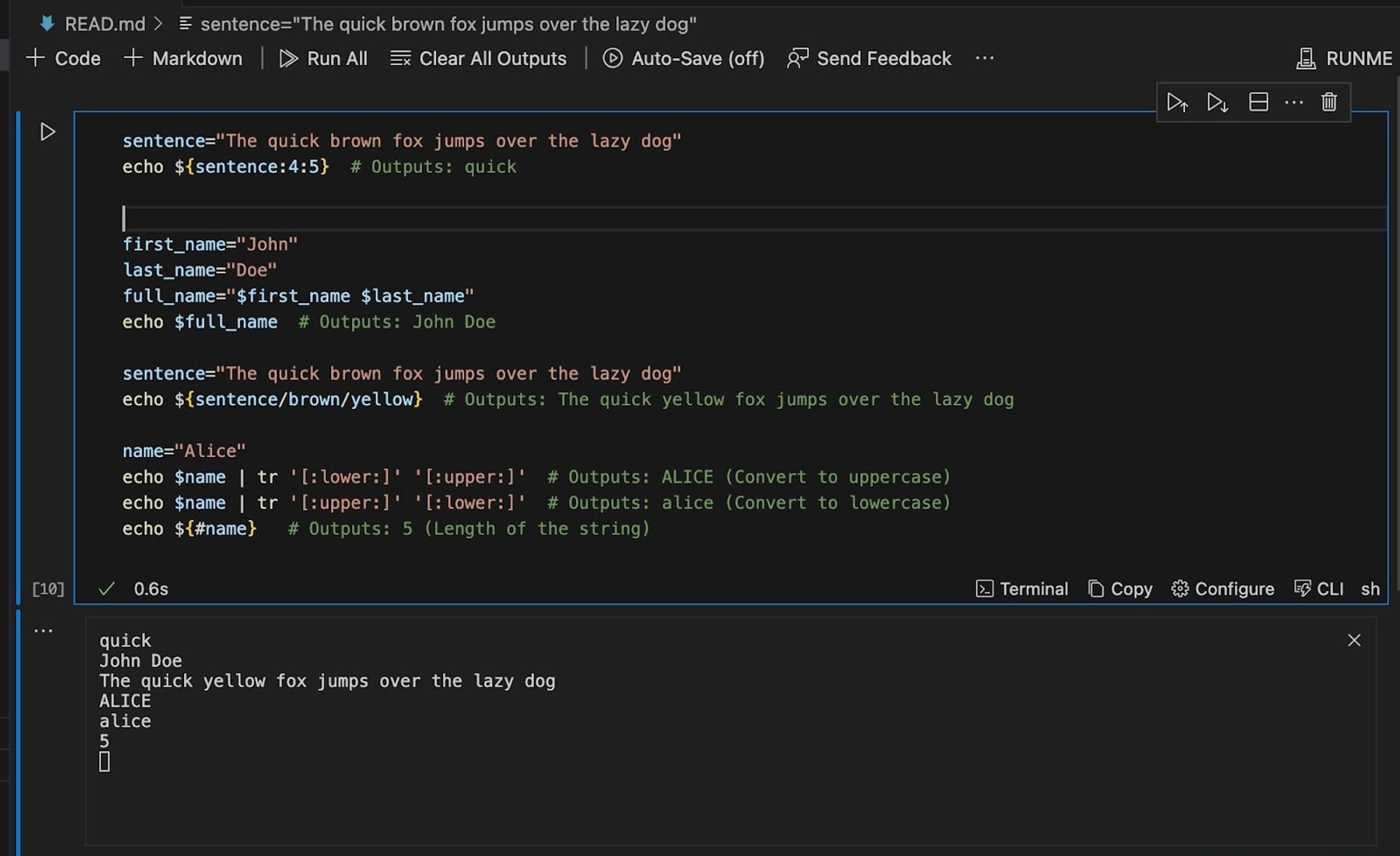
-
Conditional Statements:
If you have a series of conditional statements in a Bash script that you would love to execute, Runme makes this easy. All you need to do is create a
.mdfile in your editor, enter your script, and click the Run cell button. Run the command below to understand how this works
echo -n "Enter your score: "
read score
# Perform grade determination based on the score
if (( score >= 90 )); then
echo "Your grade is A."
elif (( score >= 80 )); then
echo "Your grade is B."
elif (( score >= 70 )); then
echo "Your grade is C."
elif (( score >= 60 )); then
echo "Your grade is D."
else
echo "Your grade is F."
fi
The image below shows how a conditional statement in a Bash script is executed in Runme in VS Code.
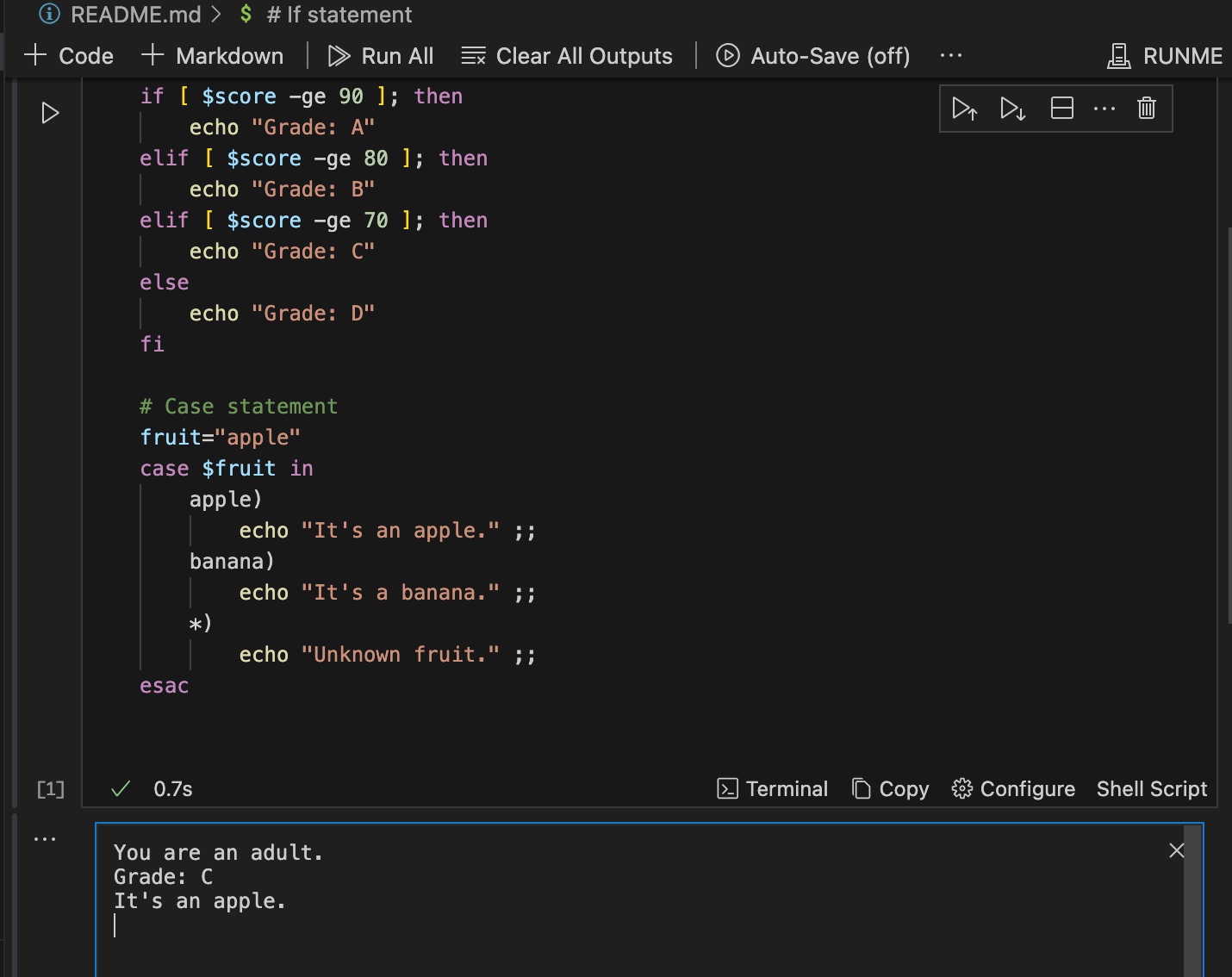
-
Integrating Runme with Docker:
You can use Runme to write several bash scripts that execute Docker commands. The script below manages a Docker container for an Nginx web server.
CONTAINER_NAME="my-nginx-container"
IMAGE_NAME="nginx:latest"
if [ "$(docker ps -a -q -f name=$CONTAINER_NAME)" ]; then
echo "Removing existing container: $CONTAINER_NAME"
docker rm -f $CONTAINER_NAME
fi
echo "Running Docker container: $CONTAINER_NAME"
docker run --name $CONTAINER_NAME -d -p 8080:80 $IMAGE_NAME
docker cp local_file.txt $CONTAINER_NAME:/usr/share/nginx/html/file.txt
docker exec $CONTAINER_NAME ls -l /usr/share/nginx/html
docker stop $CONTAINER_NAME
docker rm $CONTAINER_NAME
echo "Script Completed"
When it is executed successfully, here is the output.
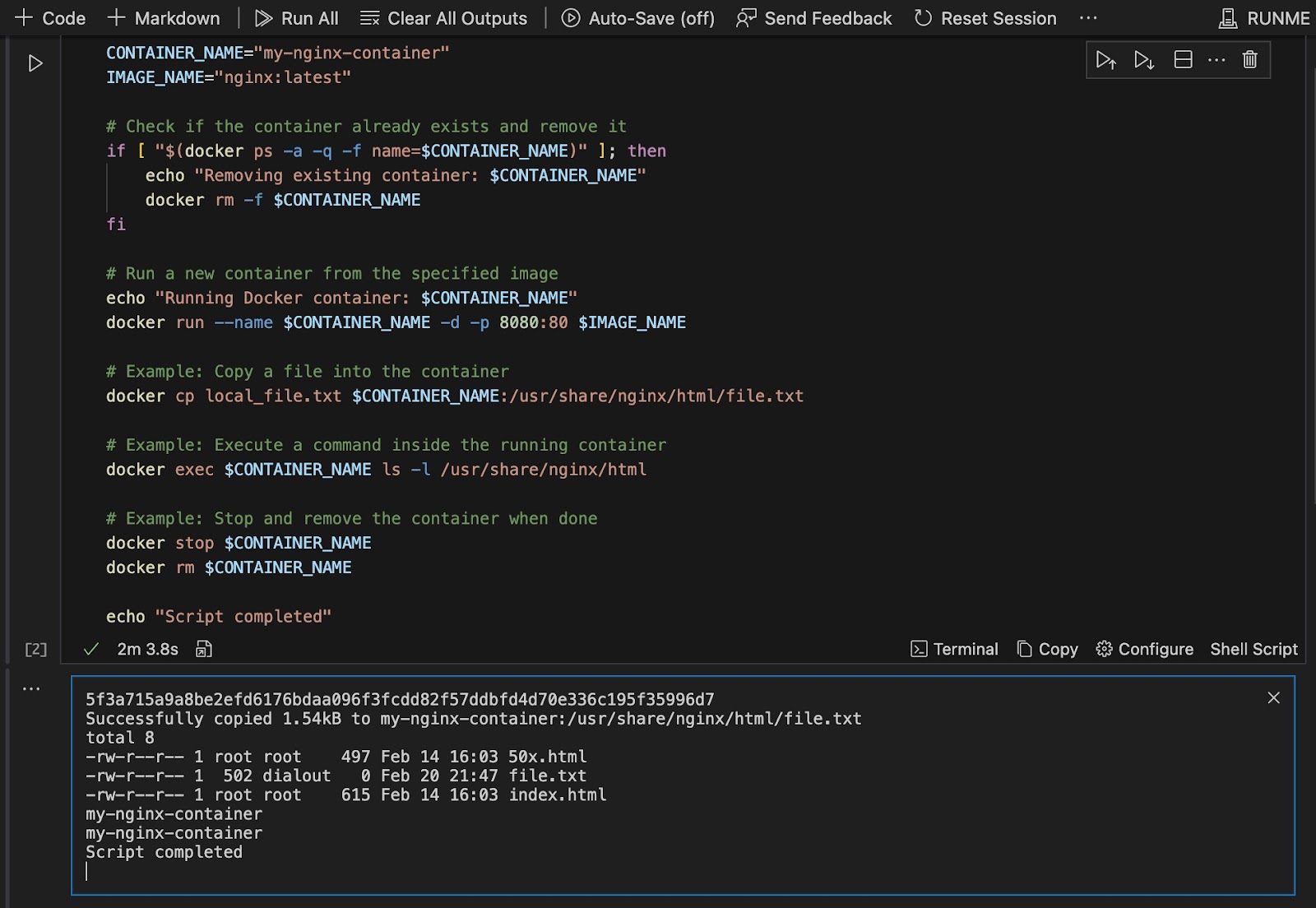
Save Your Outputs
Every output generated can be automatically saved using the Runme auto-save feature.
Runme auto-save automatically saves your outputs, enabling you to access the history of the command and all cell output produced while running your file without manual intervention.
Runme auto-save also incorporates a separate Session Outputs method that securely saves the time each cell was run and its exit codes. It stores this output in an external file for easy reference.
Note
When working with this feature, you are not to push the session outputs to git or any version control software as they have sensitive details.
Conclusion
Using Runme to execute your Bash scripts automates your process, whether it is a development, testing, or deployment task. Runme was built to enable you to automate repetitive tasks and ride off environment compatibility issues.
In this guide, we delved into how to execute your first Bash script in Runme, advanced Bash scripts you can execute in Runme, and, lastly, features in Runme that make the execution of tasks as an SRE expert, DevOps engineer, or system administrator easier.
You can easily integrate Runme with your favorite cloud-native tools. Take a look at our tutorial page to learn more ways to use Runme to make your tasks seamless.